GSC syntax & debugging
Learn the syntax for GSC including basic examples and notes to help you.
Comments
Comments exist in two ways, one-line, or multi-line block comments.
// This is a one-line comment.
/*
This is a comment across
multiple lines!
*/
Function Declaration
Declaring functions in GSC require you to give it a name, followed by a () and a bracket scope.
my_function()
{ // start of bracket scope
// [...]
} // end of bracket scope
Calling functions
GSC functions can be "threaded" or called sequentially (in logical order/sequence). If a function is "threaded", then the execution of the function being called will not hold the execution of the parent function that contains the call.
my_function()
{
print("my_other_function execution starting");
my_other_function(); // my_function() will not continue past this line until the execution of my_other_function() finishes
print("my_other_function execution completed");
print("my_other_function thread execution starting");
thread my_other_function(); // my_function() will continue past this line and carry on doing other stuff
print("my_other_function thread execution still continuing, but it's threaded");
}
my_other_function()
{
wait 3; // this function executes a 3 second wait
print("3 seconds waited");
}
/*
"my_other_function execution starting"
"3 seconds waited"
"my_other_function execution completed"
"my_other_function thread execution starting"
"my_other_function thread execution still continuing, but it's threaded"
"3 seconds waited"
*/
If you call a function on an entity, the self keyword is reversed as the entity who called the function
my_function()
{
getplayers()[0] hello_world(); // index 0 will get the first player in the game
}
hello_world() // self == player
{
self iprintln("hello world!");
}
Using variables
Variables are used to store data for the span of the current game. Variables will reset upon map rotation unless stored outside of the GSC VM context. However, for round-based gamemodes, persistent variables will keep the data through restarts.
A local variable is a variable that can be used in the whole function scope it's defined in. A variable can b e used to call a function or passed to a function via parameters. Defining a local variable is as easy as:
variable = 1;
Variables can also be global:
level.variable = 1;
or defined on an object (or entity) and be passed through to functions:
my_function()
{
variable = spawnstruct();
variable.message = "hi!";
variable print_message();
}
print_message() // self == variable
{
print(self.message);
}
/*
"hi!"
*/
Math
Math can play a huge part in gameplay scripting depending on what you are doing. The operators you can use for math in GSC include the following:
+ Addition
- Subtraction
* Multiplication
/ Division
% Modulus (Remainder)
= Equals
++ Increment (+1)
-- Decrement (-1)
+= Incrementation (requires number)
-= Decrementation (requires number)
Example some of the operations:
var++;
var--;
var += int;
var -= int;
You can also use Bitwise (Wikipedia) operations in GSC.
& Bitwise And
| Bitwise Or (inclusive or)
^ Bitwise Xor (exclusive or)
<< Left Shift
>> Right Shift
~ Bitwise NOT (one's complement)
If statements
An 'if' statement is used to see if a condition is met, and then execute code (delared in a scope) as the result. The operators you can use for comparing data in GSC include the following:
== Equal To
!= Not Equal To
! Negation (Not equal to)
< Less than
> Greater than
<= Less or Equal to
>= Greater or Equal to
&& And
|| Or
Example:
if (9 > 10)
{
print("9 is above 10");
}
else
{
print("9 is below 10");
}
/*
"9 is below 10"
*/
You can also do if statements on any sort of variables
message = "hi!";
if (message == "hi!")
{
print("hello variable!");
}
else
{
print("variable didn't say hi? :(");
}
/*
"hello variable!"
*/
The conditions can also have a "else if" to check multiple conditions
big_number = 100;
if (big_number < 20)
{
print("big number is below the number 20");
}
else if (big_number < 150)
{
print("big number is below the number 150");
}
else
{
print("big number is above the number 150");
}
/*
"big number is below the number 150"
*/
In GSC, you can check if a variable is defined with a value. This is because if a variable was undefined, and you check if it's true, it'll invoke on the condition. To do this, use the function isdefined(var), which returns true/false. If a variable equals keyword undefined or isn't defined at all, you should get false as the return type.
variable_one = 5;
variable_two = 6;
if (isdefined(variable_one))
{
print("variable_one is defined!");
variable_two = undefined; // undefined is a reserved keyword
}
if (variable_two) // the variable is undefined, but it'll still think this condition as met
{
print("variable_two claimed to be true, but is it defined?");
if (isdefined(variable_two))
{
print("is not defined");
}
else
{
print("is defined");
}
}
/*
"variable_one is defined!"
"variable_two claimed to be true, but is it defined?"
"is not defined"
*/
This is why the GSC scripts will check if a variable isdefined before checking if it is true:
if (isdefined(variable_two) && variable_two)
{
print("variable_two is defined and is true");
}
/*
"variable_two is defined and is true"
*/
In GSC, the ternary operator is also supported.
condition = (5 > 2) ? true : false;
print(condition);
/*
"true"
*/
Loops
Loops in GSC can be somewhat similar to C, but may come in different forms.
- A
whileloop is a loop that will keep looping while the condition provided is true - A
forloop is a loop that loops a set amount of times - A
foreachloop is a simplifiedforloop meant to be used on all items of an array.
while
In this example, we will check if number X is above 10.
x = 0;
while (x < 6)
{
print(va("x = %s", x));
number++;
}
print("while loop condition was met");
/*
"x = 0"
"x = 1"
"x = 2"
"x = 3"
"x = 4"
"x = 5"
"x = 6"
"while loop condition was met
*/
for
In this example, we will create an infinite loop that will never end.
my_function()
{
thread infinite_loop(); // make sure the loop you are doing doesn't halt the parent function
}
infinite_loop()
{
for(;;)
{
print("infinite loop");
wait 0.05; // infinite loops NEED to wait a server frame else your script will lag terribly or your game will crash.
}
}
foreach
In this example, we will create a loop that prints every single player in the game's name.
foreach (player in getplayers())
{
print(va("player: %s", player.name));
}
The for loop equivalent to this would be:
players = getplayers();
for (i = 0; i < players.size; i++)
{
print(va("player %s: %s", i, players[i].name));
}
Wait
GSC is ran on every server frame, and 20 server frames equal to 1 second.
wait 0.05; // 1 server frame
wait 0.5; // 10 server frames
wait 1; // 20 server frames
wait (1); // 20 server frames
Switch
Switch cases are useful for checking the case of many possibly values. This is usually recommended if you are have more than 4-5 variables as it may be faster and more organized compared to a if statement.
value = 5;
switch (value)
{
case 1:
print("value is 1");
break;
case 2:
print("value is 2");
break;
case 3:
print("value is 3");
break;
case 4:
print("value is 4");
break;
case 5:
print("value is 5");
break;
default:
print("value is not any of the cases listed");
break;
}
Events
notify
A notify event will send a cue to a endon or waittill to do something. When you notify something, it is called like <entity> notify("my_cool_notify").
endon
Knowing how a notify works, you can end threads you create easily. One of the most common notifies that occur is when a player disconnects from the game, which should be used in any player thread you run.
my_cool_player_func() // self == player
{
self endon("disconnect"); // ends when player disconnects
level endon("game_ended"); // ends when level ends game
for(;;)
{
print(va("player %s has %s kills!", self.name, self.kills));
wait 5;
}
}
waittill
A notify can also execute a waittill. A waittill is something that waits for a event to be notified, and then you can execute code off of it. If you run a waittill that isn't in a for or while, you still need a endon because the thread will never end or cause undefined behavior if so.
on_player_connect() // self == level
{
level endon("game_ended"); // ends when level ends game
for(;;)
{
level waittill("connected", player); // this is called every time a player connects
print(va("player %s has connected!", player.name));
}
}
TODO
Custom functions
With H1-mod, we add a variety of custom GSC functions and methods that are unique to the client and can assist in GSC. Below are most of the functions documented for usage.
Misc
print(message)println(message): Prints a message to the console.logprint(message): Prints a message to the game log.toupper(string): Converts all of a string to uppercase.executecommand(command): Executes a console command.replaceFunc(with, what): Replaces a script function with another script function.main()
{
replacefunc(maps\mp\gametypes\_callbacksetup::callbackVoid, ::callbackvoid_override);
}
callbackvoid_override()
{
print("callback void override was called");
}getFunction(filename, name): Gets a function from a GSC script.init()
{
function = getFunction("maps/mp/gametypes/_callbacksetup", "callbackVoid");
[[ function ]]();
}getFunctionName(function): Returns the function's name.init()
{
function = getFunction("maps/mp/gametypes/_callbacksetup", "callbackVoid");
print(getFunctionName(function)); // "maps/mp/gametypes/_callbacksetup::callbackVoid"
}say(message): Sends a chat message to all players.onPlayerConnected()
{
while (true)
{
level waittill("connected", player);
say(player.name + " connected!");
}
}entity tell(message): Sends a chat message to a player.onPlayerConnected()
{
while (true)
{
level waittill("connected", player);
player tell("Welcome back " + player.name + "!");
}
}va(string, ...): Format arguments via a format string.init()
{
server_owner = "mikey";
server_name = "Epic Server";
va_string = va("Welcome to %s's %s!", server_owner, server_name);
print(va_string); // "Welcome to mikey's Epic Server!"
}
IO
warning
IO in GSC, by default, is only used when the fs_game dvar is applied to a valid directory within the game. When the fs_game dvar is defined, IO is locked into that directory and cannot leave that directory.
However, you can opt-in to allow IO in GSC to use your root game directory folder instead. To do so, launch the game with the -allow_root_io command line argument. We DO NOT recommend using this flag or enabling it for 3rd-party mods.
fileExists(path): Returns true if the file exists.writeFile(path, data[, append]): Creates a file if it doesn't exist and writes/appends text to it.readFile(path): Reads a file.fileSize(path): Returns file size in bytes.createDirectory(path): Creates a directory.directoryExists(path): Returns true if the directory exists.directoryIsEmpty(path): Returns true if the directory is empty.listFiles(path): Returns the list of files in the directory as an array.copyFolder(source, target): Copies a folder.removeFile(path): Deletes a file if it exists.
JSON
jsonSerialize(variable[, indent]): Converts GSC variables (such as arrays) into JSON.init()
{
array = [];
array[0] = 1;
array[1] = 2;
json = jsonSerialize(array, 4);
print(json);
/*
[
2,
1
]
*/
}This function can also be useful to reveal contents of existing arrays such as
game:init()
{
print(jsonSerialize(game["round_end"]), 4);
/*
{
"draw": 1,
"round_draw": 2,
"round_win": 3,
"round_loss": 4,
"victory": 5,
"defeat": 6,
"halftime": 7,
"overtime": 8,
"roundend": 9,
"intermission": 10,
"side_switch": 11,
"match_bonus": 12,
"tie": 13,
"game_end": 14,
"spectator": 15,
}
*/
}jsonParse(json): Converts JSON into a GSC variable.init()
{
array = jsonParse("[1, 2, 3, 4]");
print(array[0] + " " + array[1] + " " + array[2] + " " + array[3]);
/*
1 2 3 4
*/
}jsonPrint(...): Prints values as json.map(...): Creates a string-indexed array.init()
{
array = map("first", 1, "second", 2);
print(jsonSerialize(array, 4));
/*
{
"first": 1,
"second": 2
}
*/
}
Debugging
assert(condition):assertex(condition, error): Throws an error if condition is false.type(variable)typeof(variable): Returns the name of the type of variable.
Script errors
GSC is a scripting language that is prone to errors very easily. When undefined behavior occurs, it'll just keep going the best it can. For example, when a variable is undefined but used in a if statement, it'll run the code as if the variable was true. This runtime error below shows the instruction that is failing, and then the function & file.
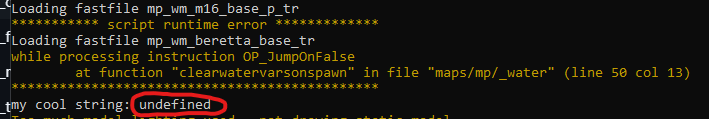
For some reason, it's not showing the name & function it's erroring in while I write this up, but the line information is correct and we can break it down from there. So using the information, we can conclude the variable at line 50 is undefined.
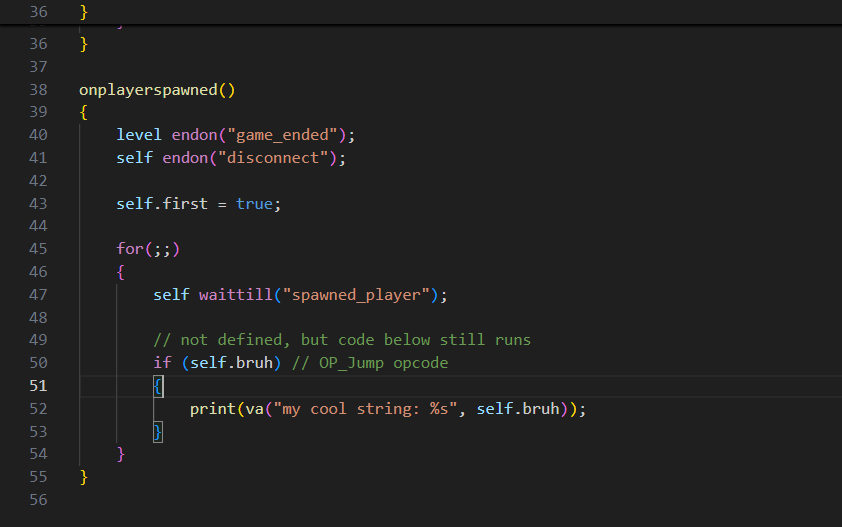
Stuff like this makes people think their mod is working because they don't get runtime errors normally, but in reality, it's just working by luck. In H1-Mod, we restore a dvar known as developer_script. When you set this dvar to 1, and start or map_restart a game, you will get debug information about the script including runtime errors that'll show errors in your script.
Opcodes
Some of the opcode instructions that show might be confusing, but they're usually straightforward. Below is a list of very common opcodes and how to fix them. The common theme between all of these is that a variable being checked is undefined, therefore needs a definition somewhere or you need logic to check if isdefined before you do stuff with it.
| Opcode | Reason |
|---|---|
| OP_EvalSelfFieldVariable | Trying to access a field like self.bruh that might be undefined |
| OP_SetLevelFieldVariableField | Trying to set a field on the level object |
| OP_CastBool | A variable being casted to bool is undefined |
| OP_JumpOnFalse | If condition failing, usually commonly a undefined variable. |
| OP_JumpOnTrue | Same as OP_JumpOnFalse |
| OP_ScriptMethodThreadCallPointer | Most common reason is the caller is undefined |
| OP_CallBuiltinMethod | A builtin engine method is failing due to bad parameters |
| OP_inequality | A != is failing, meaning one or both of the variables might be undefined |
| OP_equality | A == is failing, meaning one or both of the variables might be undefined |
| OP_greater | A > is failing, meaning one or both of the variables might be undefined |
| OP_greater_equal | A >= is failing, meaning one or both of the variables might be undefined |
| OP_less | A < is failing, meaning one or both of the variables might be undefined |
| OP_less_equal | A <= is failing, meaning one or both of the variables might be undefined |
| OP_inc | A variable += 1 or variable++ is failing, meaning the variable is undefined |
| OP_plus | A + is failing, meaning one or both of the variables might be undefined |
| OP_divide | A / is failing, meaning one or both of the variables might be undefined |
| OP_multiply | A * is failing, meaning one or both of the variables might be undefined |
| OP_GetSelfObject | Self is undefined, this should never happen |
| OP_SetVariableField | Setting a field on a variable that's not a entity is failing. Variable may be undefined |
| OP_endon | Variable being used on a endon is undefined |
| OP_notify | Variable being used on a notify is undefined |
| OP_waittill | Variable being used on a waittill is undefined |
| OP_wait | Time for a wait is failing, if variable is used probably undefined |
| OP_EvalArray | Trying to do variable[index] fails, variable might be undefined |
| OP_switch | The variable for the switch case table is undefined |
| OP_size | Doing variable.size fails due to variable being undefined |
| OP_checkclearparams | Too many parameters might be getting passed to the function, or not the required ones |
| OP_BoolNot | Doing a inverse of variable like variable = !variable meaning undefined variable |
Variable leaks
Variable leaks are when so much undefined behavior is happening that the game starts leaking variables. The GSC VM only has so many variables it can allocate, and for stability on a dedicated server, you must write good code. This can happen for various reasons, including more than just undefined variables. Threads that run waittill, for loops, or even while loops per player or level can easily leak if you are not properly ending them when the game ends, or when exitlevel is called.
The errors that occurs will be something along the lines of "child/parent variables maxed out". For example, this function below shows a function calls by a player that waits until the game is over, and then runs some code.
waittill_game_end() // self == player
{
//self endon("disconnect"); // let's act like our code doesn't have this
level endon("shutdownGame_called"); // absolute last notify to end threads
level waittill("game_ended");
print(va("%s has %s kills when game is ended", self.name, self.kills));
}
This function may look alright, but there are already some issues that can occur. If a player leaves the game, this code will still run. When that happens, the game will cry about "removed entity" errors because the player no longer exists. You now have a variable leak! To fix this, you add a self endon("disconnect"); so the thread ends when a player leaves.
Each function you create should always include a endon for game_ended, or shutdownGame_called if you need to end it at the very last second of the match. If it's a player thread, it should always endon disconnect for the player entity.